
GMP EU Grades A, B, C, D Cleanroom Classifications PDF Download with ISO and FED-STD-209E Equivalents
Our printable PDF poster on GMP EU Grades A-D Cleanroom Classifications offers a detailed chart comparing GMP EU Grades A, B, C, and D with ISO standards and FED-STD-209E. It also includes expert recommendations for the appropriate cleanroom wipes and apparel for each classification.
In the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, maintaining a clean environment is critical to ensure the safety of personnel and integrity of products. Cleanrooms are classified based on the concentration of airborne particles, and different standards exist to define these classifications. The most commonly referenced standards are the GMP EU Grades, ISO Standards, and the now-superseded FED-STD-209E. Understanding these classifications and their equivalences can help manufacturers maintain compliance and optimize their cleanroom operations.
Cleanroom Classifications Explained
GMP EU Grades: These are the European guidelines for Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) specific to sterile medicinal products. They classify cleanrooms into four grades: A, B, C, and D. Each grade represents a different level of air cleanliness, with Grade A being the most stringent.
ISO Standards: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides a globally recognized framework for cleanroom classifications. The ISO 14644-1 standard specifies the concentration limits for airborne particulate cleanliness for different ISO classes, ranging from ISO Class 1 (most stringent) to ISO Class 9.
FED-STD-209E: The Federal Standard 209E was a U.S. standard for cleanroom classification, which has been superseded by ISO standards but is still widely recognized in historical contexts. This standard classified cleanrooms based on the maximum allowable number of particles per cubic foot of air.
Equivalence of Cleanroom Classifications
To effectively manage cleanroom environments, it's essential to understand how these classifications correspond to each other. Here is a comparative chart that outlines the equivalences between GMP EU Grades, ISO Classes, and FED-STD-209E classifications:
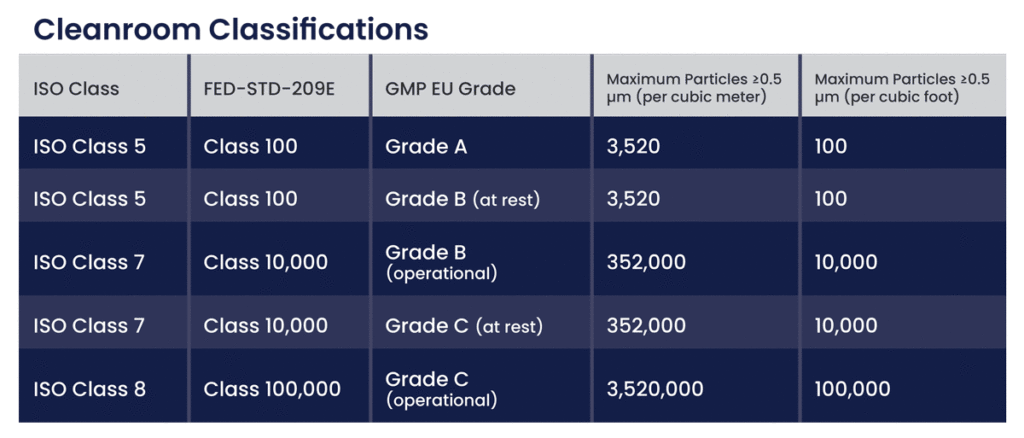
Key Considerations for Each Cleanroom Classification
Grade A / ISO Class 5 / FED-STD-209E Class 100: This is the highest level of cleanliness and is typically required for high-risk operations such as aseptic processing and filling. The stringent particle limits ensure minimal risk of contamination, making it suitable for critical areas where sterile products are exposed.
Grade B (at rest) / ISO Class 5 / FED-STD-209E Class 100: Similar to Grade A, this classification is used for aseptic preparation and filling but in the background cleanroom areas. It maintains the same high standards of cleanliness to support the critical Grade A environments.
Grade B (operational) / ISO Class 7 / FED-STD-209E Class 10,000: When in operation, the cleanroom must meet less stringent particle counts than at rest but still maintains a high level of cleanliness to prevent contamination during production.
Grade C (at rest) / ISO Class 7 / FED-STD-209E Class 10,000: This classification is used for less critical stages of sterile product manufacturing. The at-rest state requires maintaining a significant level of cleanliness to prepare for more critical operations.
Grade C (operational) / ISO Class 8 / FED-STD-209E Class 100,000: During operations, the cleanroom can accommodate higher particle counts than when at rest but must still ensure a controlled environment to support subsequent critical stages.
Grade D / ISO Class 8 / FED-STD-209E Class 100,000: This is the least stringent classification and is used for general cleanroom environments where the risk of contamination is lower. It serves as a preparation area for more critical cleanroom grades.
Implementing and Maintaining Cleanroom Standards
Achieving and maintaining these cleanroom standards requires a comprehensive approach, including regular environmental monitoring, stringent personnel hygiene protocols, and robust contamination control strategies. Here are some key practices:
- Environmental Monitoring: Regularly measure airborne particulate levels to ensure compliance with the specified cleanroom classification. Use particle counters and microbial air samplers to monitor and record data.
- Personnel Training: Ensure that all personnel are trained in proper gowning procedures, cleanroom behavior, and contamination control techniques. Regular refresher courses and assessments help maintain high standards.
- Contamination Control: Implement effective contamination control measures, such as airlocks, HEPA filtration systems, and proper material transfer protocols. Regularly review and update procedures to address new risks and incorporate technological advancements.
Conclusion
Understanding the equivalence between GMP EU Grades, ISO Classes, and FED-STD-209E classifications is essential for maintaining a controlled and compliant cleanroom environment. By adhering to these standards, pharmaceutical and biotechnology manufacturers can ensure the quality and safety of their sterile products, ultimately protecting patient health. At Blue Thunder Technologies, we provide the necessary cleanroom supplies and expertise to help you achieve and maintain these high standards. Contact us today to learn more about our solutions for contamination control and cleanroom management.