Personnel Grounding - Basic ESD Control Principles
Personnel working with sensitive electronic products must be protected against producing and receiving electrostatic discharge (ESD) — the effects of static electricity. ESD affects both worker safety and company profitability if it is not addressed properly.
It is important to implement approved ESD grounding requirements specific to areas where grounding is necessary by first identifying areas in need of grounding. These areas include:
- Manufacturing floors
- Work benches
- Packing and shipping centers
- Clean rooms
- Research and development labs
Determine General ESD Grounding Requirements
A project’s grounding requirements are driven by the size of a workspace and the type of work being done. Smaller work environments are required to adhere to basic ESD grounding, which, in practice, provides a two-step grounding solution for personnel and work equipment.
Basic steps are:
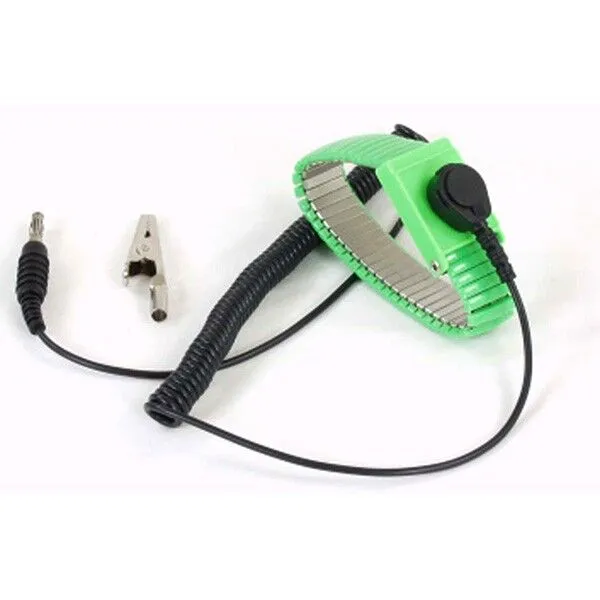
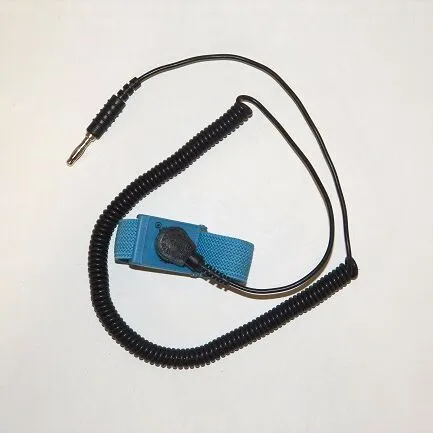
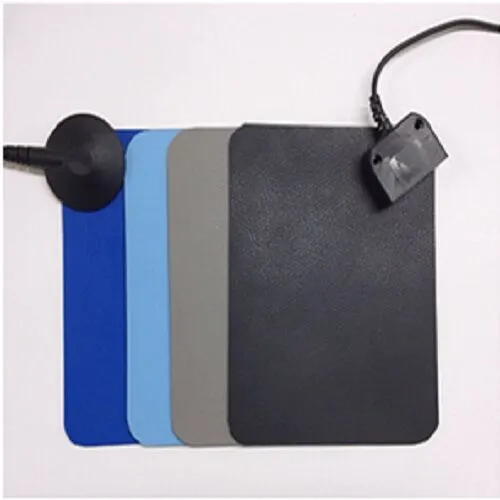
- Connect all equipment and personnel to a common ground point like a grounding wrist strap, a dissipative work mat, or other solutions that dissipate static charge, and
- Connect the common ground point to a grounding conductor.
Hospitals and larger facilities require more rigorous requirements due to the probability that they contain flammable and/or explosive gasses that are highly susceptible to static electrical events.
Specific ESD Requirements for Clean Room Personnel
Electrical grounding to prevent personnel and equipment from generating a static charge is a requirement of clean room environments. Both the human body and stainless steel are conductive surfaces and require specially designed solutions like an ESD floor combined with conductive footwear to prevent the accumulation of static charges on personnel. Wrist straps wired to a grounding point also provide protection from ESD.
Grounding works by connecting a sufficiently conductive surface (like the human body or stainless steel) to a grounding point that will discharge the static into the earth. A specially-designed ESD floor combined with conductive footwear will prevent static charges from accumulating on personnel. Wrist straps wired to a grounding point will provide similar protection. Partitioning workstations and ensuring that individual workstations are protected areas is often necessary as well.
Implementing some form of static control program to protect personnel and equipment from generating static charges is simply good business policy. A written procedure coupled with the right set of grounding techniques will help to prevent injury to personnel as well as catastrophic failure, upset failure, and latent defects. All of these are costly and cause scrapping of a product or, in the case of upset failures, software glitches and latent defects that shorten the life of a product and, over time, increase warrantied replacement costs.
Get in touch with Blue Thunder Technologies for help finding or implementing solutions to these problems so that you can save time and money.